Bring financial literacy to life in your classroom
Videos to help you get started
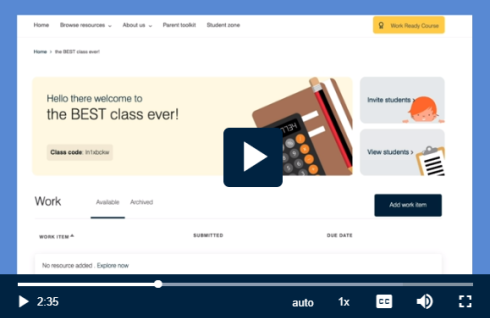
Video: Creating a class in Tax, Super + You (teachers)

Flexible resources for Australian teachers and students
Use our educator developed activities complete with instructions and resources to deliver the curriculum or pick and choose from hundreds of resources to develop your own teaching and learning programs.
Explore featured activities
See what Australian teachers have been using recently across our curriculum-aligned activities. You can create a class, assign activities to your classes and monitor student work.
Plan your lesson how you like, we don’t impose rules.
You can pick and choose the resources you incorporate into your own teaching and learning programs.
Stay in the loop
Catch up with the latest news and tips in ATO Education.
LATEST NEWS

Have you heard of our Work Ready Course?
Support your Year 10-12 students to understand and navigate the tax and super systems from the day they start work to the day they retire.
Go to the courseExplore our video collection
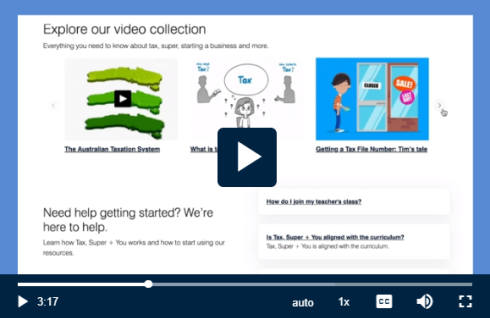
Everything you need to know about tax, super, starting a business and more.
Need help getting started? We’re here to help.
Learn how Tax, Super + You works and how to start using our resources.